Address
Kaypian, San Jose Del Monte City, Bulacan Philippines
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 8AM - 6PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
Kaypian, San Jose Del Monte City, Bulacan Philippines
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 8AM - 6PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM


Integrated HR. Accurate Payroll.


Integrated HR. Accurate Payroll.
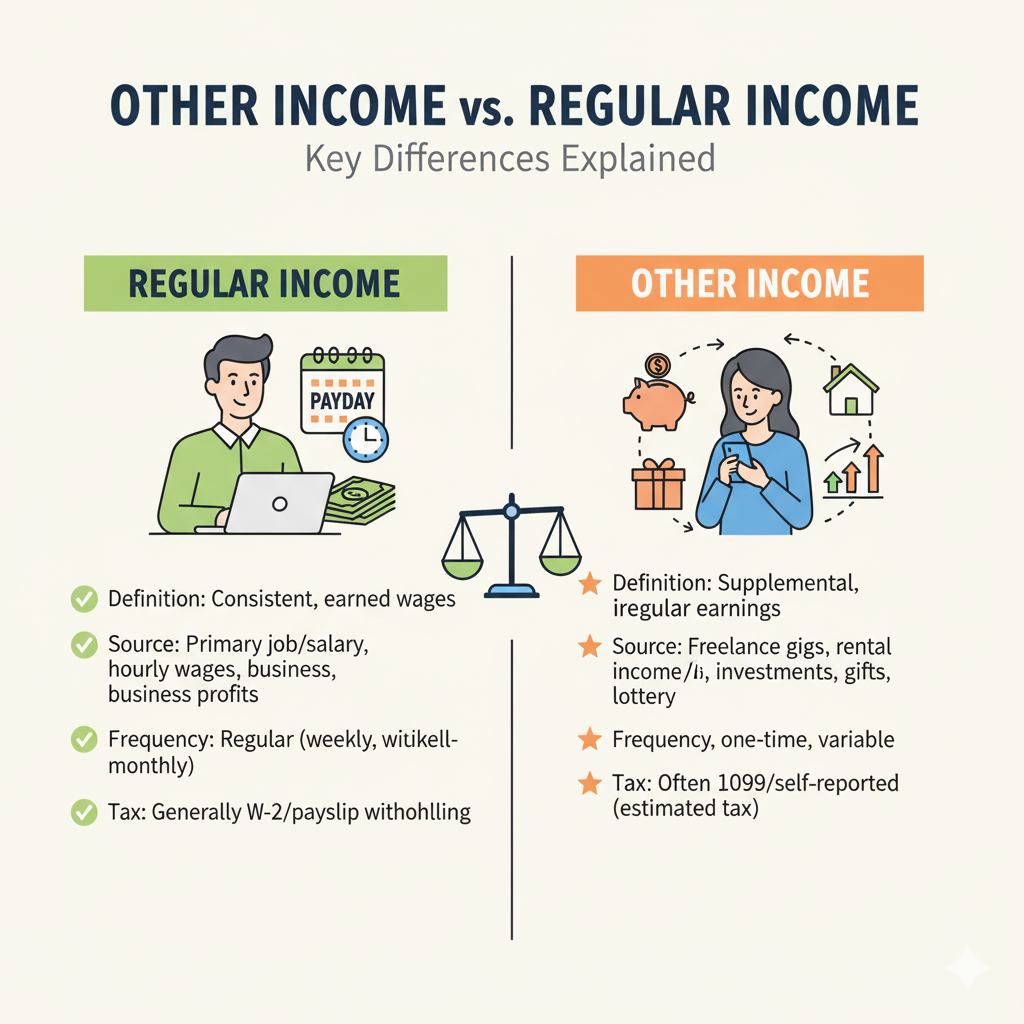
When it comes to payroll and taxes, not all income is treated the same way. You may see the terms regular income and other income on your payslip or tax return. While both contribute to your total earnings, they are categorized differently — and that affects how you get paid, how much tax you owe, and how employers process payroll.
In this guide, we’ll explain the key differences between other income and regular income, with examples and tax implications for both employees and employers.
Regular income refers to the fixed and recurring earnings you receive from your main employment. It is the core of your paycheck and usually follows a predictable schedule.
Examples of Regular Income:
Monthly salary or hourly wages
Overtime pay
Holiday pay
Allowances included in payroll
Standard commissions (if part of employment contract)
📌 Key Feature: Regular income is directly tied to your employment contract and is subject to standard payroll deductions such as taxes, social security, and health contributions.
Other income includes any additional earnings outside of your regular salary or wages. It is often irregular, non-recurring, or from sources unrelated to your main job.
Examples of Other Income:
Freelancing or part-time side jobs
Rental income from property
Dividends, interest, or investment returns
Royalties from books, music, or patents
Bonuses, honoraria, or one-time incentives
Lottery winnings or awards
📌 Key Feature: Other income may be taxed differently, sometimes at special tax rates or as part of annual declarations, depending on local laws.
While both regular income and other income contribute to your financial well-being, they differ in source, frequency, and tax treatment. Regular income offers stability and automatic payroll deductions, while other income provides flexibility and extra earnings — but requires careful tracking for taxes.
By understanding the distinction, employees can plan finances better, and employers can ensure payroll compliance with transparency and accuracy.