Address
Kaypian, San Jose Del Monte City, Bulacan Philippines
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 8AM - 6PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
Kaypian, San Jose Del Monte City, Bulacan Philippines
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 8AM - 6PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM


Integrated HR. Accurate Payroll.


Integrated HR. Accurate Payroll.
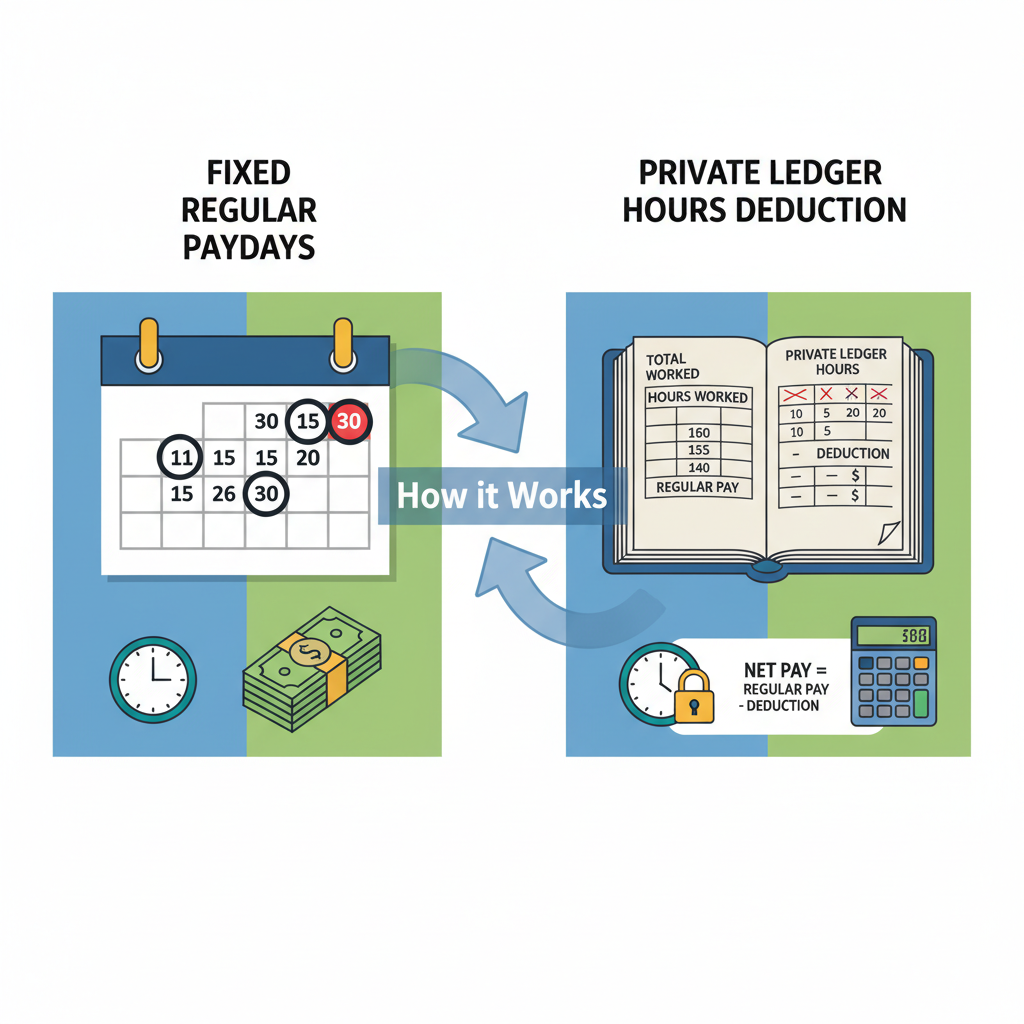
Accurate payroll management is essential for maintaining employee trust and ensuring business compliance. One area that often creates confusion is Private Ledger Hours Deduction, especially when employees are paid on fixed regular paydays. Understanding how this works helps businesses avoid disputes, maintain transparency, and ensure employees are paid fairly.
In this article, we’ll explain what private ledger hours deduction means, how it functions alongside fixed regular paydays, and why it’s important for payroll accuracy.
Private Ledger Hours Deduction is the process of subtracting non-working hours (such as absences, tardiness, or unpaid leaves) from an employee’s recorded time in the payroll ledger. This ensures employees are compensated based on actual work hours rather than only scheduled time.
The “private ledger” serves as an internal payroll record used by HR and accounting teams to document time, attendance, and salary adjustments.
Fixed regular paydays mean employees are paid on a consistent schedule, such as:
This structure provides employees with predictable pay, but it also requires precise hours tracking to ensure fairness and compliance.
Example:
Scheduled hours per pay cycle: 80 hours
Deducted (absences, tardiness): 8 hours
Payable hours: 72 hours
Private Ledger Hours Deduction is an essential process for businesses with fixed regular paydays. It ensures that payroll is fair, accurate, and compliant with labor laws while maintaining employee trust.
By combining clear policies, transparent systems, and modern HRIS solutions, companies can simplify payroll processes and avoid costly mistakes.
If your business still relies on manual tracking, now is the time to upgrade to a dedicated HRIS & Payroll System that automates ledger hours deduction and ensures seamless payday processing.