Address
Kaypian, San Jose Del Monte City, Bulacan Philippines
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 8AM - 6PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
Kaypian, San Jose Del Monte City, Bulacan Philippines
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 8AM - 6PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM


Integrated HR. Accurate Payroll.


Integrated HR. Accurate Payroll.
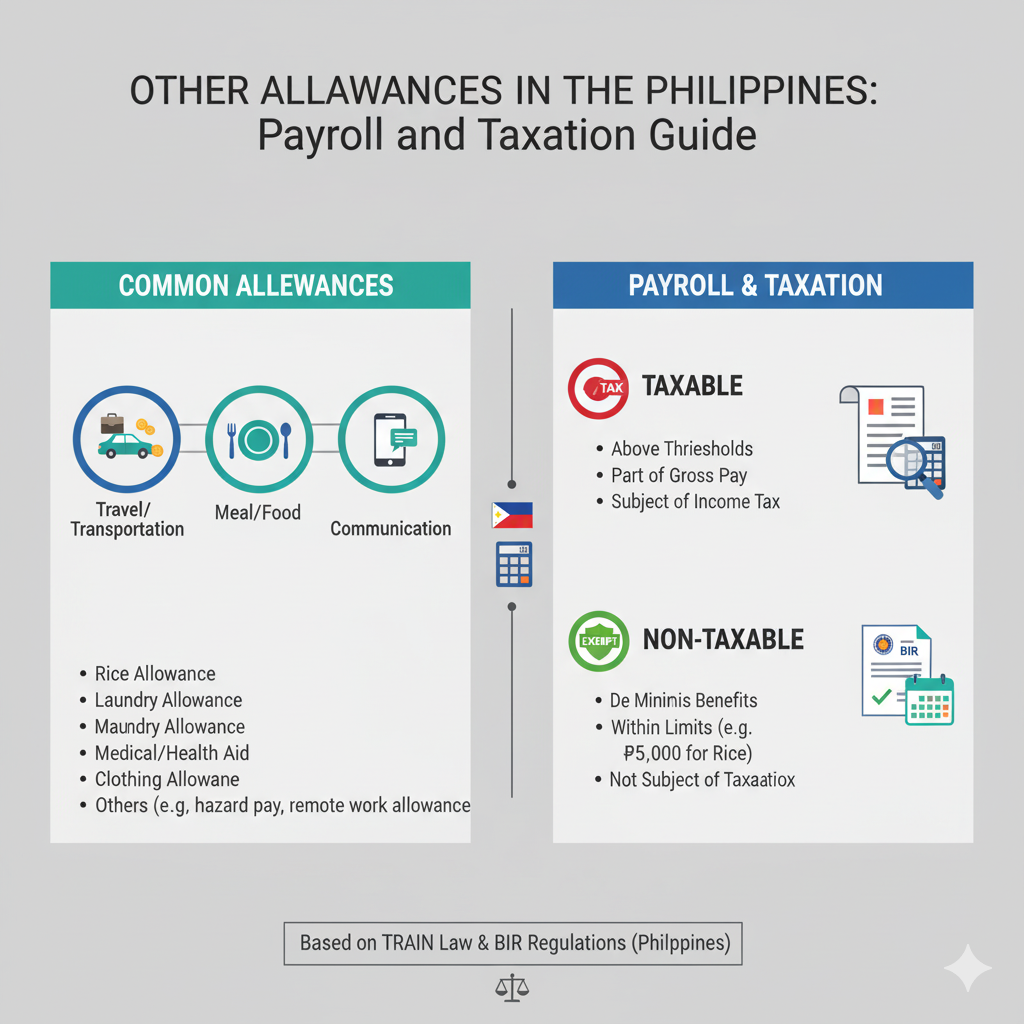
When looking at your payslip in the Philippines, you might notice a section labeled “Other Allowance.” Many employees are unsure what it covers, how it differs from basic pay or benefits, and whether it’s taxable.
This guide explains what other allowance means in payroll, examples in Philippine companies, and the taxation rules under BIR (Bureau of Internal Revenue).
In the Philippines, other allowance refers to additional compensation or benefits that employees receive outside their basic salary. It usually falls under fringe benefits or supplementary pay, depending on its purpose.
Examples of Other Allowance:
📌 Key Point: Other allowance is meant to support employees’ work-related expenses or provide extra financial benefits.
Taxation depends on the type of allowance and whether it is considered part of compensation or a de minimis benefit.
The BIR exempts certain allowances from tax if they fall under de minimis benefits and within the prescribed limits, such as:
Uniform and clothing allowance (not exceeding ₱6,000/year)
Meal allowance (not exceeding 25% of minimum wage)
Rice subsidy (up to ₱2,000/month)
Medical cash allowance (up to ₱1,500/semester for children)
Allowances exceeding BIR limits or considered part of additional compensation are taxable. For example:
Transportation allowance beyond the exempt ceiling
Large representation allowances
Special allowances not categorized as de minimis
📌 Tip for Employers: Always check Revenue Regulations 5-2011 and BIR updates for current exemption limits.
Employers in the Philippines must:
In the Philippines, other allowance is an important part of payroll that goes beyond basic salary. While some allowances are tax-free as de minimis benefits, others are taxable depending on BIR regulations.
For both employees and employers, understanding how allowances are classified ensures financial clarity, proper tax compliance, and smoother payroll management.